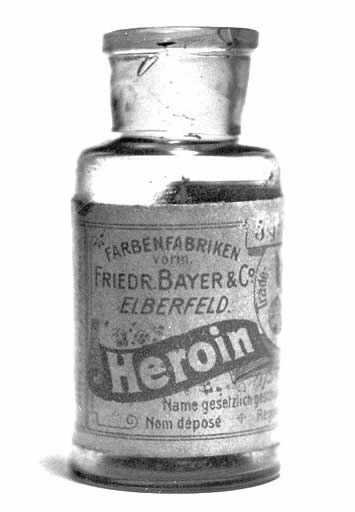
There’s been a shift in our culture (at least in US) towards seeing medication as a sign of weakness from one of alleviation of suffering that predominated out society some 100 years ago. Some people I know are even proud of the fact that they’ve never taken a painkiller or were treated for cough. Stoicism became a virtue all in itself — “I’m a good person because I don’t take medicine, preferring to suffer the illness and/or the symptoms of the disease.” And it’s not just the patients that feel this way. Medical professionals routinely prescribe to the “complain 3 times” rule: their patients have to mention being in pain on multiple visits prior to getting a prescription that would deal with it. A friend told a story of a doctor visit during which he was told that “he didn’t want to appear to be complainer.” Several weeks later, he was having back surgery and remains in a wheelchair to this day, a decade later! How did we get here? This is a very complicated question, but it might help to examine how things use to be. Below are medications as they were packaged and sold all over America in the…


